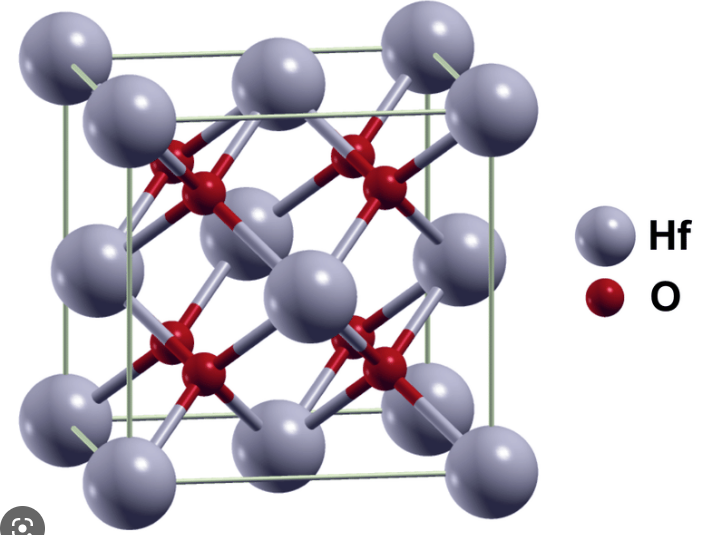
Introduction: Hafnium dioxide (HfO2) is a metal oxide compound that is commonly used in electronic devices as a high-k dielectric material. Its crystal structure of it is cubic (figure1).
Cubic phase HfO2. Hf is in FFC position
Some of its key properties include:
- High
dielectric constant: HfO2 has a high dielectric constant (k), which means
that it can store a large amount of electric charge per unit area. This
property is important for electronic devices because it allows for the
creation of capacitors that can store more charge in a smaller area.
- Good
thermal stability: HfO2 is stable at high temperatures, which makes it
suitable for use in devices that operate at elevated temperatures.
- Good
electrical properties: HfO2 has a high breakdown voltage and low leakage
current, which are important for ensuring that electronic devices are
reliable and have a long lifespan.
- High
refractive index: HfO2 has a high refractive index, which makes it useful
for creating optical coatings and thin films for applications such as
solar cells and LEDs.
- Compatibility
with silicon technology: HfO2 is compatible with silicon technology, which
makes it easy to integrate into existing electronic devices.
What are the physical properties of HfO2?
Hafnium oxide (HfO2) is a chemical compound that has several
physical properties, including:
Density: HfO2 has a density of approximately 9.68 g/cm³ at room
temperature.
Melting point: The melting point of HfO2 is very high, around 2,760°C or 4,999°F.
Hardness: HfO2 is a very hard material, with a Mohs hardness of
approximately 7.5.
Refractive index: The refractive index of HfO2 is around 2.1, which
means that it has a relatively high level of optical clarity.
Thermal conductivity: HfO2 has a high thermal conductivity, which
means that it can conduct heat very effectively.
Electrical conductivity: HfO2 is an insulator, meaning it does not
conduct electricity well.
Color: HfO2 is typically white or off-white in color.
Solubility: HfO2 is not soluble in water or organic solvents.
Dielectric properties of HfO2?
Hafnium oxide (HfO2) is a high-k dielectric material, which means
it has a high relative permittivity or dielectric constant (εr). Here are some
dielectric properties of HfO2:
- Dielectric
constant: HfO2 has a high dielectric constant ranging from 20 to 25, which
is significantly higher than that of conventional SiO2 dielectrics.
- Dielectric
loss: HfO2 has low dielectric loss, which makes it suitable for use in
high-frequency applications.
- Breakdown
strength: HfO2 has a high breakdown strength, which makes it resistant to
electrical breakdown under high voltage stress.
- Leakage
current: HfO2 has low leakage current density, which means that it can
store charge for longer periods of time.
These dielectric properties make HfO2 an attractive material for use as a gate dielectric in metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) and as a dielectric in capacitors. HfO2-based dielectrics have enabled further miniaturization of electronic devices and improved their performance.
These physical and dielectric properties make HfO2 a useful material in various applications, including as a high-temperature electrical insulator, as a thermal barrier coating, and in the production of optical coatings and components. Overall, HfO2 is a versatile material with a range of useful properties that make it well-suited for use in electronic devices and other applications find more help here.
No comments:
Post a Comment